|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .devcontainer | ||
| .github | ||
| assets | ||
| backends | ||
| benchmark | ||
| clients/python | ||
| docs | ||
| integration-tests | ||
| launcher | ||
| load_tests | ||
| nix | ||
| proto | ||
| router | ||
| server | ||
| .dockerignore | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .pre-commit-config.yaml | ||
| .redocly.lint-ignore.yaml | ||
| CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md | ||
| CONTRIBUTING.md | ||
| Cargo.lock | ||
| Cargo.toml | ||
| Dockerfile | ||
| Dockerfile.nix | ||
| Dockerfile_amd | ||
| Dockerfile_intel | ||
| Dockerfile_trtllm | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| Makefile | ||
| README.md | ||
| crate-hashes.json | ||
| flake.lock | ||
| flake.nix | ||
| rust-toolchain.toml | ||
| sagemaker-entrypoint.sh | ||
| tgi-entrypoint.sh | ||
| update_doc.py | ||
README.md
Text Generation Inference


A Rust, Python and gRPC server for text generation inference. Used in production at Hugging Face to power Hugging Chat, the Inference API and Inference Endpoint.
Table of contents
Text Generation Inference (TGI) is a toolkit for deploying and serving Large Language Models (LLMs). TGI enables high-performance text generation for the most popular open-source LLMs, including Llama, Falcon, StarCoder, BLOOM, GPT-NeoX, and more. TGI implements many features, such as:
- Simple launcher to serve most popular LLMs
- Production ready (distributed tracing with Open Telemetry, Prometheus metrics)
- Tensor Parallelism for faster inference on multiple GPUs
- Token streaming using Server-Sent Events (SSE)
- Continuous batching of incoming requests for increased total throughput
- Messages API compatible with Open AI Chat Completion API
- Optimized transformers code for inference using Flash Attention and Paged Attention on the most popular architectures
- Quantization with :
- Safetensors weight loading
- Watermarking with A Watermark for Large Language Models
- Logits warper (temperature scaling, top-p, top-k, repetition penalty, more details see transformers.LogitsProcessor)
- Stop sequences
- Log probabilities
- Speculation ~2x latency
- Guidance/JSON. Specify output format to speed up inference and make sure the output is valid according to some specs..
- Custom Prompt Generation: Easily generate text by providing custom prompts to guide the model's output
- Fine-tuning Support: Utilize fine-tuned models for specific tasks to achieve higher accuracy and performance
Hardware support
- Nvidia
- AMD (-rocm)
- Inferentia
- Intel GPU
- Gaudi
- Google TPU
Get Started
Docker
For a detailed starting guide, please see the Quick Tour. The easiest way of getting started is using the official Docker container:
model=HuggingFaceH4/zephyr-7b-beta
# share a volume with the Docker container to avoid downloading weights every run
volume=$PWD/data
docker run --gpus all --shm-size 1g -p 8080:80 -v $volume:/data \
ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:2.4.1 --model-id $model
And then you can make requests like
curl 127.0.0.1:8080/generate_stream \
-X POST \
-d '{"inputs":"What is Deep Learning?","parameters":{"max_new_tokens":20}}' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json'
You can also use TGI's Messages API to obtain Open AI Chat Completion API compatible responses.
curl localhost:8080/v1/chat/completions \
-X POST \
-d '{
"model": "tgi",
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a helpful assistant."
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is deep learning?"
}
],
"stream": true,
"max_tokens": 20
}' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json'
Note: To use NVIDIA GPUs, you need to install the NVIDIA Container Toolkit. We also recommend using NVIDIA drivers with CUDA version 12.2 or higher. For running the Docker container on a machine with no GPUs or CUDA support, it is enough to remove the --gpus all flag and add --disable-custom-kernels, please note CPU is not the intended platform for this project, so performance might be subpar.
Note: TGI supports AMD Instinct MI210 and MI250 GPUs. Details can be found in the Supported Hardware documentation. To use AMD GPUs, please use docker run --device /dev/kfd --device /dev/dri --shm-size 1g -p 8080:80 -v $volume:/data ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:2.4.1-rocm --model-id $model instead of the command above.
To see all options to serve your models (in the code or in the cli):
text-generation-launcher --help
API documentation
You can consult the OpenAPI documentation of the text-generation-inference REST API using the /docs route.
The Swagger UI is also available at: https://huggingface.github.io/text-generation-inference.
Using a private or gated model
You have the option to utilize the HF_TOKEN environment variable for configuring the token employed by
text-generation-inference. This allows you to gain access to protected resources.
For example, if you want to serve the gated Llama V2 model variants:
- Go to https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens
- Copy your cli READ token
- Export
HF_TOKEN=<your cli READ token>
or with Docker:
model=meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct
volume=$PWD/data # share a volume with the Docker container to avoid downloading weights every run
token=<your cli READ token>
docker run --gpus all --shm-size 1g -e HF_TOKEN=$token -p 8080:80 -v $volume:/data ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:2.4.1 --model-id $model
A note on Shared Memory (shm)
NCCL is a communication framework used by
PyTorch to do distributed training/inference. text-generation-inference make
use of NCCL to enable Tensor Parallelism to dramatically speed up inference for large language models.
In order to share data between the different devices of a NCCL group, NCCL might fall back to using the host memory if
peer-to-peer using NVLink or PCI is not possible.
To allow the container to use 1G of Shared Memory and support SHM sharing, we add --shm-size 1g on the above command.
If you are running text-generation-inference inside Kubernetes. You can also add Shared Memory to the container by
creating a volume with:
- name: shm
emptyDir:
medium: Memory
sizeLimit: 1Gi
and mounting it to /dev/shm.
Finally, you can also disable SHM sharing by using the NCCL_SHM_DISABLE=1 environment variable. However, note that
this will impact performance.
Distributed Tracing
text-generation-inference is instrumented with distributed tracing using OpenTelemetry. You can use this feature
by setting the address to an OTLP collector with the --otlp-endpoint argument. The default service name can be
overridden with the --otlp-service-name argument
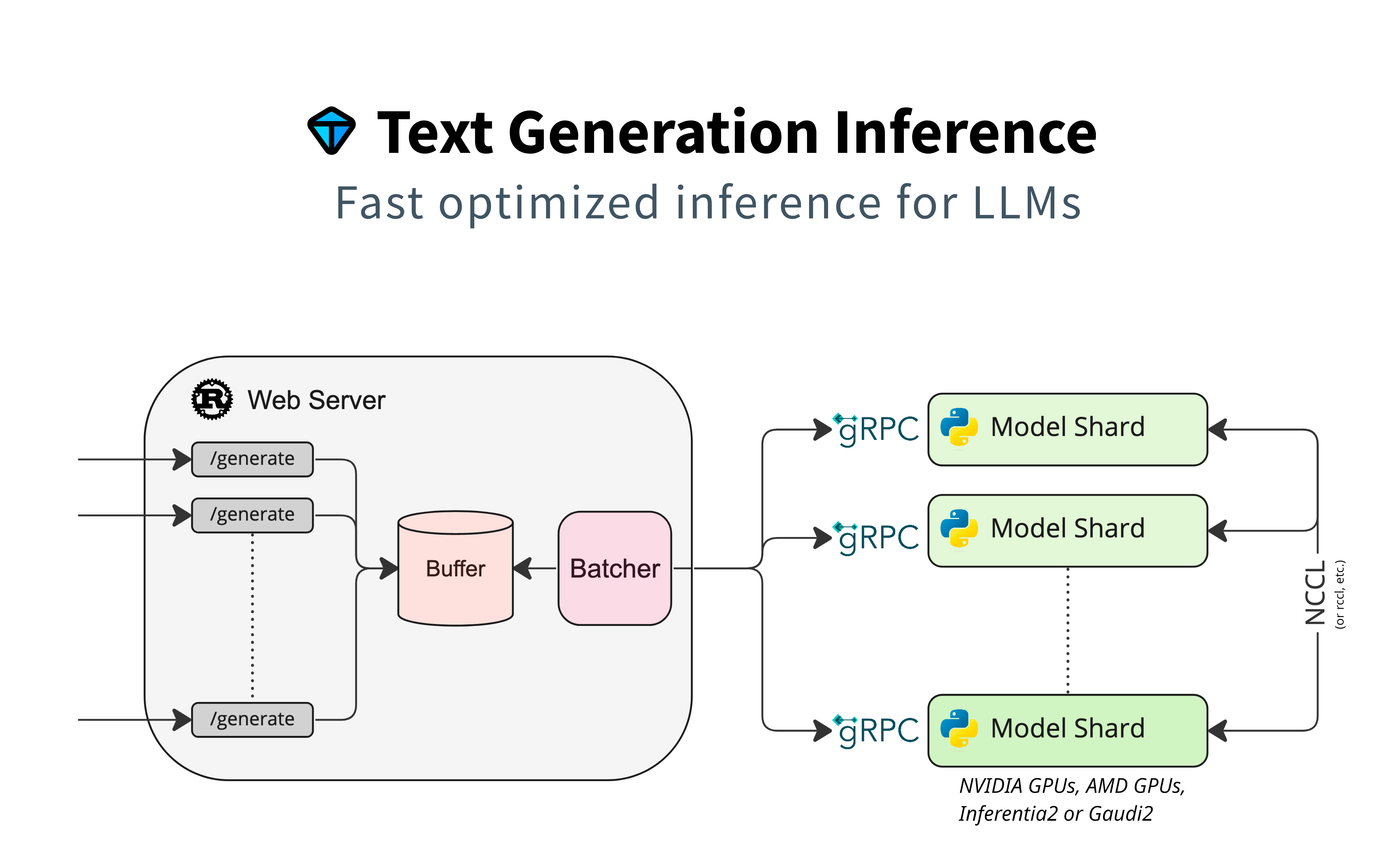
Architecture
Detailed blogpost by Adyen on TGI inner workings: LLM inference at scale with TGI (Martin Iglesias Goyanes - Adyen, 2024)
Local install
You can also opt to install text-generation-inference locally.
First install Rust and create a Python virtual environment with at least
Python 3.9, e.g. using conda:
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh
conda create -n text-generation-inference python=3.11
conda activate text-generation-inference
You may also need to install Protoc.
On Linux:
PROTOC_ZIP=protoc-21.12-linux-x86_64.zip
curl -OL https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf/releases/download/v21.12/$PROTOC_ZIP
sudo unzip -o $PROTOC_ZIP -d /usr/local bin/protoc
sudo unzip -o $PROTOC_ZIP -d /usr/local 'include/*'
rm -f $PROTOC_ZIP
On MacOS, using Homebrew:
brew install protobuf
Then run:
BUILD_EXTENSIONS=True make install # Install repository and HF/transformer fork with CUDA kernels
text-generation-launcher --model-id mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2
Note: on some machines, you may also need the OpenSSL libraries and gcc. On Linux machines, run:
sudo apt-get install libssl-dev gcc -y
Local install (Nix)
Another option is to install text-generation-inference locally using Nix. Currently,
we only support Nix on x86_64 Linux with CUDA GPUs. When using Nix, all dependencies can
be pulled from a binary cache, removing the need to build them locally.
First follow the instructions to install Cachix and enable the TGI cache. Setting up the cache is important, otherwise Nix will build many of the dependencies locally, which can take hours.
After that you can run TGI with nix run:
nix run . -- --model-id meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct
Note: when you are using Nix on a non-NixOS system, you have to make some symlinks to make the CUDA driver libraries visible to Nix packages.
For TGI development, you can use the impure dev shell:
nix develop .#impure
# Only needed the first time the devshell is started or after updating the protobuf.
(
cd server
mkdir text_generation_server/pb || true
python -m grpc_tools.protoc -I../proto/v3 --python_out=text_generation_server/pb \
--grpc_python_out=text_generation_server/pb --mypy_out=text_generation_server/pb ../proto/v3/generate.proto
find text_generation_server/pb/ -type f -name "*.py" -print0 -exec sed -i -e 's/^\(import.*pb2\)/from . \1/g' {} \;
touch text_generation_server/pb/__init__.py
)
All development dependencies (cargo, Python, Torch), etc. are available in this dev shell.
Optimized architectures
TGI works out of the box to serve optimized models for all modern models. They can be found in this list.
Other architectures are supported on a best-effort basis using:
AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(<model>, device_map="auto")
or
AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(<model>, device_map="auto")
Run locally
Run
text-generation-launcher --model-id mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2
Quantization
You can also run pre-quantized weights (AWQ, GPTQ, Marlin) or on-the-fly quantize weights with bitsandbytes, EETQ, fp8, to reduce the VRAM requirement:
text-generation-launcher --model-id mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2 --quantize
4bit quantization is available using the NF4 and FP4 data types from bitsandbytes. It can be enabled by providing --quantize bitsandbytes-nf4 or --quantize bitsandbytes-fp4 as a command line argument to text-generation-launcher.
Read more about quantization in the Quantization documentation.
Develop
make server-dev
make router-dev
Testing
# python
make python-server-tests
make python-client-tests
# or both server and client tests
make python-tests
# rust cargo tests
make rust-tests
# integration tests
make integration-tests